The Ganga River System









The Ganga River System
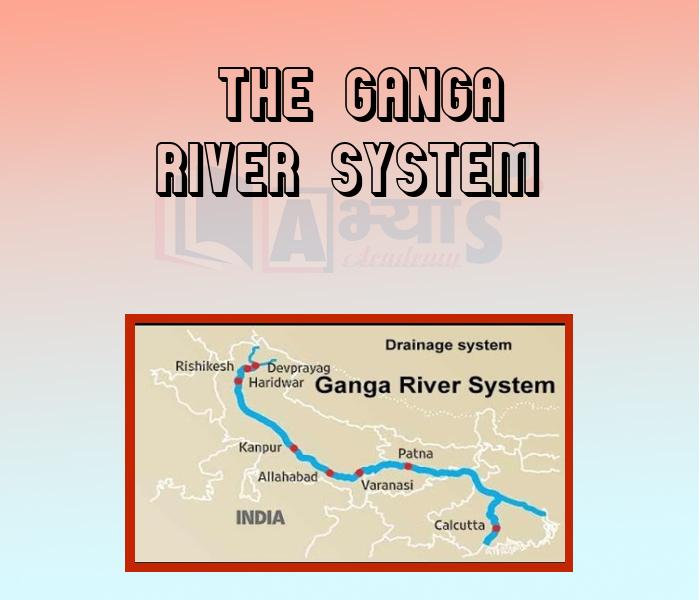
The Ganga River System:
This system starts as the Bhagirathi (Headwaters of Ganga) being fed by the Gangotri glacier in Uttarakhand. It is joined by the Alaknanda river at Devaprayag to form the Ganga. At Haridwar, the Ganga emerges from the mountains on to the plains. Many of the Ganga’s tributaries like the Yamuna, Ghaghara, Gandak and Kosi are major rivers which flow down from the Himalayas. The river Yamuna rises from the Yamunotri glacier in the Himalayas. It flows parallel to the Ganga as a right bank tributary. It meets the Ganga at Allahabad. The Ghaghara, the Gandak and the Kosi rise in the Nepal Himalayas. Every year they flood parts of the Northern plains, causing destruction and damage to life and property, but also enriching the soil of agricultural lands. The Ganga’s main tributaries which come from the Peninsular uplands are the Chambal, the Betwa and the Son. These rise from semi-arid areas, have shorter courses and do not carry much water in them. The Ganga flows eastwards till Farakka in West Bengal. Here it divides into two branches and, forms a distributary known as the Bhagirathi-Hooghly (also called Hughli), which flows Southward to Kolkata and the Bay of Bengal. The main stream of the Ganga flows into Bangladesh, where it is joined by the Brahmaputra coming from Assam to form the Meghna. This mighty river system, flows into the Bay of Bengal. This forms the Sunderban delta when it reaches the Bay of Bengal.
Ganga plain lies between rivers __________________ | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
'Bhagirathi' is the headwaters of the Ganga. It is fed by which of the following glaciers? | |||
| Right Option : B | |||
| View Explanation | |||
By what name is the Ganga known in Bangladesh? | |||
| Right Option : A | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
A marvelous experience with Abhyas. I am glad to share that my ward has achieved more than enough at the Ambala ABHYAS centre. Years have passed on and more and more he has gained. May the centre flourish and develop day by day by the grace of God.

Archit Segal
7thI have spent a wonderful time in Abhyas academy. It has made my reasoning more apt, English more stronger and Maths an interesting subject for me. It has given me a habbit of self studying

Yatharthi Sharma
10thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.

Shivam Rana
7thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.
